Concave Mirror
Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of three distinct rays from a point on the object:
X) a ray parallel to the principal axis reflected through F (the principal focus)
Y) a ray passing through C which is then reflected back along its original path
Z) a ray passing through F, which is then reflected parallel to the principal axis
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Z) a ray passing through F, which is then reflected parallel to the principal axis
Click on the diagram below to play!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Object's position (S), focal point (F) | Image | Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| S < F (Object between focal point and mirror) |
|  |
| S = F (Object at focal point) |  | |
| F < S < 2F (Object between focus and centre of curvature) |
| 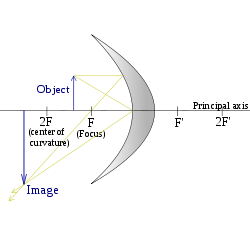 |
| S = 2F (Object at centre of curvature) |
|  |
| S > 2F (Object beyond centre of curvature) |
| 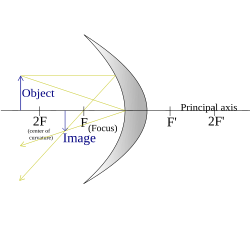 |
 This is ME
This is ME






0 comments:
Post a Comment